Melanoma Skin Cancer: Symptoms & Treatment in London
Expert melanoma skin cancer treatment in London. Learn about symptoms, diagnosis, and personalised care from Dr James Wilson


Jump to:
- What is Melanoma Skin Cancer?
- Understanding Melanoma
- How Melanoma Differs from Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer
- Symptoms of Melanoma
- Common Signs and Symptoms
- Additional Warning Signs
- Types of Melanoma
- Superficial Spreading Melanoma
- Nodular Melanoma
- Lentigo Maligna Melanoma
- Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
- Amelanotic Melanoma
- Ocular Melanoma
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Risk Factors for Melanoma
- Causes of Melanoma
- Diagnosis and Staging
- How Melanoma is Diagnosed
- Staging Melanoma
- Treatment Options for Melanoma
- Main Treatment Modalities
- Advanced Treatment Options
- Clinical Trials and Emerging Treatments
- The Role of a Multidisciplinary Team
- How Dr James Wilson Can Help
- Overview of Services for Melanoma
- Why Choose My Practice
- Private Healthcare Advantages
- Prevention and Early Detection
- Preventing Melanoma
- Early Detection Strategies
- The Importance of Regular Monitoring
- Melanoma Treatment: A Personalised Approach
- Treatment by Stage
- Integrating Multiple Treatment Modalities
- Living with Melanoma
- Managing Treatment Side Effects
- Emotional Support and Resources
- Long-term Follow-up Care
- Understanding Treatment Outcomes
- Survival Rates by Stage
- Factors Affecting Prognosis
- Success with Modern Treatments
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What does melanoma skin cancer look like?
- Is melanoma skin cancer curable?
- How fast does melanoma skin cancer spread?
- What causes melanoma skin cancer?
- How do I know if I have melanoma skin cancer?
- Can melanoma skin cancer be inherited?
- What are the survival rates for melanoma?
- Does melanoma skin cancer itch?
- How is melanoma skin cancer treated?
- Is melanoma the most dangerous skin cancer?
- Take the Next Step in Your Melanoma Care
- Scheduling Your Consultation
- What to Expect
- Contact Information
If you’ve been diagnosed with melanoma skin cancer or have concerns about changing moles, expert care is essential. Early detection and advanced treatment can dramatically improve outcomes. I’m Dr James Wilson, a leading Clinical Oncologist in London specialising in comprehensive melanoma treatment. I offer immediate access to cutting-edge therapies including immunotherapy, targeted treatments, and precision radiotherapy to give you the best possible chance of cure or long-term control.
What is Melanoma Skin Cancer?
Melanoma skin cancer develops when melanocytes—the skin cells that produce pigment—begin growing abnormally. Unlike other types of skin cancer, melanoma has the potential to spread to other parts of the body if not detected and treated early. However, when caught in its early stages, melanoma is highly treatable with excellent cure rates.
Understanding Melanoma
Melanoma, also known as malignant melanoma or cutaneous melanoma, represents the most serious type of skin cancer. While it accounts for only about 1% of all skin cancers, it causes the majority of skin cancer deaths. The cancer cells can develop from an existing mole or appear as a new mole on normal-looking skin.
How Melanoma Differs from Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer
Non-melanoma skin cancer includes basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. These cancers rarely spread to other parts of the body and have excellent cure rates with appropriate treatment. Melanoma, however, has a higher risk of spreading to nearby lymph nodes and other organs if not caught early, making prompt diagnosis and treatment crucial.
Symptoms of Melanoma
Recognising the symptoms of melanoma skin cancer can save your life. Early melanoma often appears as changes to existing moles or the development of new, unusual spots on the skin.
Remember that skin cancer treatments are more effective the earlier they are given. Don’t delay in having any worrying skin lesions checked. Even if your doctor reassures you that you have a normal mole, it’s better to be safe than sorry!
It’s important to be aware of the signs of skin cancer. Remember that skin cancer prevention is always preferable to needing a cure.
Common Signs and Symptoms
The most common sign of melanoma is a change in an existing mole or the appearance of a new mole. The ABC warning signs are:
- Asymmetry: One half of a mole doesn’t match the other half
- Border irregularity: Edges are ragged, blurred, or irregular shape
- Colour variation: Uneven colour with shades of brown, black, red, white, or blue
- Diameter: Moles larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser)
- Evolution: Any mole that’s changing in size, shape, colour, or texture
Additional Warning Signs
Other symptoms of melanoma include:
- A sore that doesn’t heal
- Spreading of pigment beyond the border of a spot
- Redness or swelling beyond the border
- Change in sensation, such as itchiness or tenderness
- Bleeding from a mole or dark spot
Types of Melanoma
Understanding the different types of melanoma helps inform treatment decisions and prognosis. Each type has distinct characteristics and may require tailored approaches to treatment.
Superficial Spreading Melanoma
Superficial spreading melanoma is the most common type of melanoma, accounting for about 70% of cases. This type typically grows slowly along the top layer of skin before penetrating deeper. It often develops from an existing mole and can occur anywhere on the body, though it’s more common on the torso in men and legs in women.
Nodular Melanoma
Nodular melanoma is the second most common type, representing about 15-20% of melanomas. This aggressive form grows quickly downward into deeper skin layers. It often appears as a raised, dark-coloured bump and may not follow the typical ABCDE warning signs, making early detection more challenging.
Lentigo Maligna Melanoma
Lentigo maligna melanoma typically affects older people and develops in areas of the body that have had significant sun exposure over many years, particularly the face and neck. It often begins as a flat, brown or black spot that grows slowly over time.
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
Acral lentiginous melanoma occurs on the palms of hands, soles of feet, or under fingernails and toenails. This type is more common in people with dark skin and can be particularly challenging to detect as it appears in areas not typically associated with sun exposure.
Amelanotic Melanoma
Amelanotic melanoma lacks typical pigmentation, appearing pink, red, or flesh-coloured rather than brown or black. This absence of colour can make it difficult to recognise, as it may resemble other non-cancerous skin conditions.
Ocular Melanoma
Ocular melanoma develops in the eye, most commonly in the uvea (the middle layer of the eye wall). While rare, this type of melanoma requires specialised treatment and careful monitoring for potential spread to other organs.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes melanoma and the risk factors involved helps with both prevention and early detection strategies.
Risk Factors for Melanoma
Several factors can increase your risk of developing melanoma skin cancer:
UV Radiation and Sun Exposure
Ultraviolet radiation from the sun and artificial sources like tanning beds represents the primary risk factor for melanoma. UV light damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to cancerous changes. Even occasional intense sun exposure that results in sunburn significantly increases melanoma risk.
Family History of Skin Cancer
Having a family history of melanoma increases your risk, with some inherited genetic mutations making individuals more susceptible. If you have a family history of melanoma, regular skin checks become even more important.
Pale Skin and Other Physical Traits
People with fair skin, light hair, and blue eyes have a higher risk of melanoma due to lower levels of protective melanin. However, melanoma can affect people of all skin types, including those with dark skin.
Weakened Immune System
Individuals with compromised immune systems, whether due to medical conditions or immunosuppressive medications following organ transplant, face increased melanoma risk.
Multiple Moles
Having many moles (more than 50) or atypical moles increases melanoma risk. People with numerous moles should have regular professional skin examinations.
Causes of Melanoma
Role of UV Radiation in DNA Damage
UV radiation causes direct damage to the DNA within skin cells. When this damage accumulates faster than the cell’s repair mechanisms can fix it, cancerous changes may occur. Both UVA and UVB radiation contribute to melanoma development.
Genetic Mutations
Certain genetic mutations can predispose individuals to melanoma. These may be inherited (present from birth) or acquired (developing over time due to environmental factors). Understanding your genetic risk can help guide screening and prevention strategies.
Diagnosis and Staging
Accurate diagnosis and staging of melanoma are crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment approach and predicting outcomes.
How Melanoma is Diagnosed
Visual Inspection and Dermoscopy
The diagnostic process begins with a thorough visual examination of your skin. Dermoscopy - a specialised magnifying tool - is used to examine suspicious lesions in detail. This technique allows me to see features not visible to the naked eye.
Biopsy and Further Tests
If a lesion appears suspicious, a biopsy is performed to obtain tissue for microscopic examination. The biopsy results confirm whether melanoma is present and provide important information about the cancer’s characteristics.
For confirmed melanoma cases, additional tests may include:
- Sentinel lymph node biopsy: To determine if cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes
- CT scan: To check for spread to internal organs
- Blood tests: To assess general health and organ function
- PET scan: Advanced imaging to detect cancer spread throughout the body
Staging Melanoma
Stages of Melanoma
Melanoma staging helps determine treatment options and prognosis:
Stage 0 (Melanoma in situ): Cancer cells are only in the top layer of skin
Stage I: Early-stage melanoma confined to the skin
Stage II: Larger or thicker melanomas that haven’t spread to lymph nodes
Stage III: Melanoma that has spread to nearby lymph nodes or skin
Stage IV: Advanced melanoma that has spread to distant parts of the body (metastatic melanoma)
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection dramatically improves melanoma outcomes. Stage I melanomas have cure rates exceeding 95%, while advanced melanoma requires more intensive treatment approaches. Regular skin self-examinations and professional skin checks are vital for catching melanoma in its early stages.
Treatment Options for Melanoma
Modern melanoma treatment has been revolutionised by advances in immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and precision radiotherapy. Treatment options depend on the stage and characteristics of your specific melanoma.
Main Treatment Modalities
Surgical Excision
Surgical excision remains the main treatment for most melanomas. The procedure involves removing the melanoma along with a margin of healthy tissue to ensure complete removal. For early-stage melanomas, surgery alone may be curative way to treat melanoma.
Radiation Therapy
Radiotherapy plays an important role in comprehensive melanoma care, particularly for:
- Controlling symptoms from metastatic melanoma
- Treating areas where surgery isn’t feasible
- Reducing the risk of recurrence in high-risk cases
I specialise in advanced radiotherapy techniques including:
- Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT): Ultra-precise targeting of melanoma deposits
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS): Highly effective for brain metastases
- MR-linac therapy: Revolutionary technology combining MRI guidance with radiation delivery
Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy
These breakthrough treatments have transformed outcomes for advanced melanoma:
Immunotherapy: Enhances your immune system’s ability to recognise and attack cancer cells. Key medications include pembrolizumab, nivolumab, and ipilimumab.
Targeted Therapy: For melanomas with specific genetic mutations (such as BRAF mutations), targeted drugs like dabrafenib and trametinib can be highly effective.
Advanced Treatment Options
Stereotactic Radiotherapy
Stereotactic radiotherapy represents one of the most significant advances in melanoma treatment. This highly precise technique delivers concentrated radiation doses to melanoma deposits while sparing healthy tissue. I use this approach to treat:
- Brain metastases with exceptional control rates
- Metastases in the spine, liver, and other organs
- Areas where surgery would be too risky
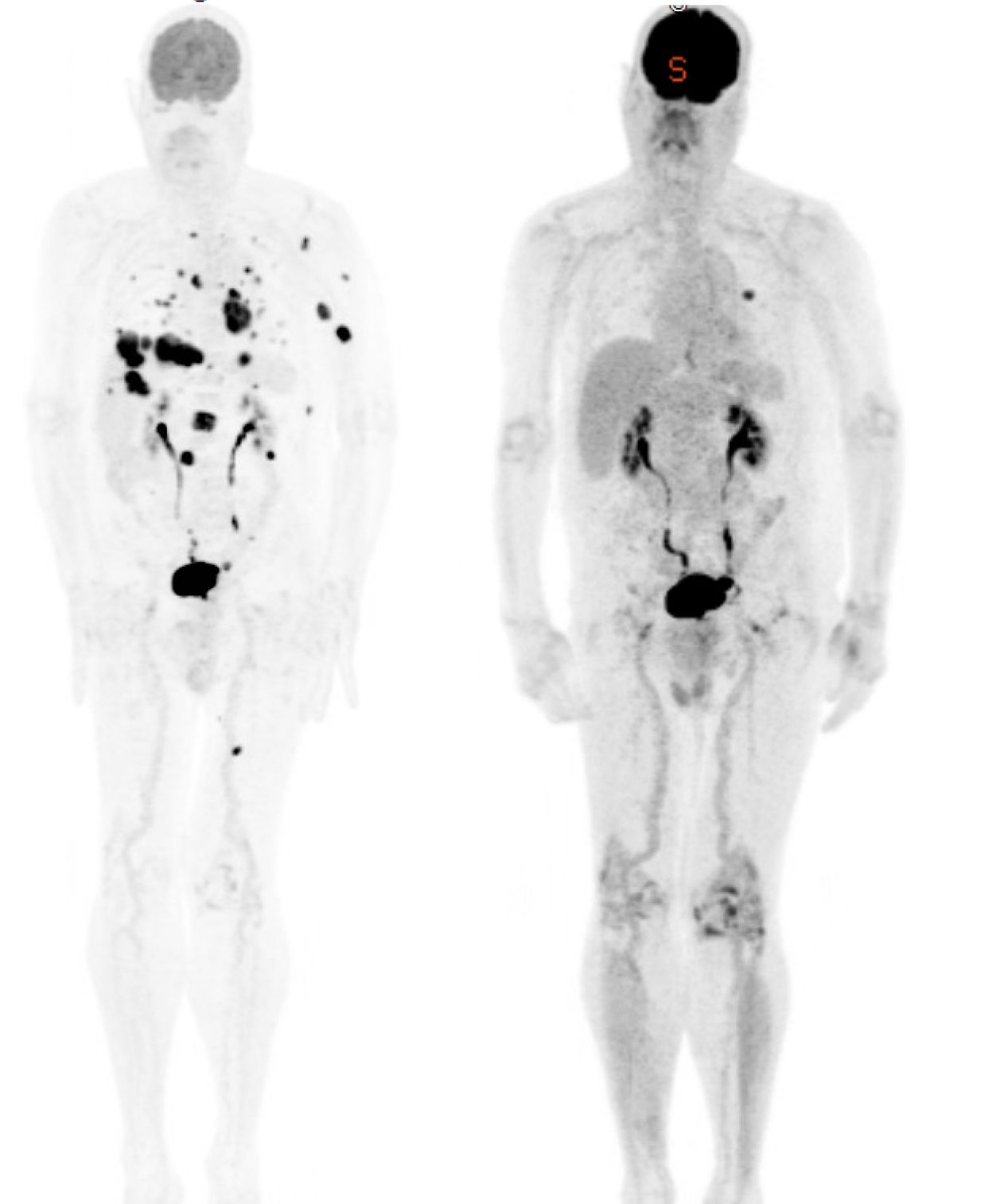
Recent PET scan imaging from my practice demonstrates the remarkable response achievable with modern immunotherapy treatments, showing complete resolution of previously active melanoma deposits throughout the body.
Proton Beam Therapy
For select patients, proton beam therapy offers advantages over conventional radiation. This advanced technique can reduce radiation exposure to healthy organs, particularly important when treating melanoma near critical structures.
CyberKnife
CyberKnife technology provides sub-millimetre accuracy for treating melanoma metastases. This robotic system can track tumour movement during treatment, ensuring precise delivery even in challenging locations.
MR Linac
The MR-linac represents the pinnacle of precision radiotherapy. By combining real-time MRI imaging with radiation delivery, this technology allows for exceptional accuracy and the ability to adapt treatment based on daily changes in tumour position and size.
Breakthrough Drug Therapies
Modern drug treatments for melanoma include:
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: These drugs remove the brakes from your immune system, allowing it to attack melanoma more effectively. Examples include pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and nivolumab (Opdivo).
BRAF and MEK Inhibitors: For melanomas with BRAF mutations, combinations like dabrafenib plus trametinib can produce rapid and dramatic responses.
Combination Approaches: Using multiple immunotherapy drugs together or combining immunotherapy with targeted therapy can enhance treatment effectiveness.
Clinical Trials and Emerging Treatments
Overview of Current Clinical Trials for Melanoma
Access to clinical trials can provide opportunities to receive the latest investigational treatments before they become widely available. These studies are conducted under strict ethical guidelines and may offer hope for patients with advanced disease.
Promising New Treatments
Emerging treatments under investigation include:
- Novel immunotherapy combinations
- CAR-T cell therapies adapted for melanoma
- Oncolytic virus therapies
- Advanced vaccine approaches
Multidisciplinary Approach
Comprehensive melanoma care requires coordination between multiple specialists to ensure the best possible outcomes.
The Role of a Multidisciplinary Team
Effective melanoma treatment involves collaboration between:
- Clinical oncologists specialising in melanoma
- Dermatologists for diagnosis and skin monitoring
- Surgical oncologists for complex procedures
- Pathologists for accurate diagnosis
- Radiologists for advanced imaging
- Specialist nurses for ongoing support
How Our Team Collaborates
I work closely with leading specialists across London to ensure you receive comprehensive care. This multidisciplinary approach means:
- Faster diagnosis and staging
- Coordinated treatment planning
- Access to the full range of treatment options
- Seamless care transitions between specialists
- Ongoing monitoring and follow-up
How Dr James Wilson Can Help
As a leading melanoma specialist in London, I offer comprehensive care that combines cutting-edge treatments with personalised attention.
Overview of Services for Melanoma
My melanoma services include:
- Rapid consultation and diagnosis
- Advanced staging investigations
- Personalised treatment planning
- Access to the latest immunotherapy and targeted therapy options
- State-of-the-art radiotherapy techniques
- Clinical trial access when appropriate
- Long-term follow-up and monitoring
Why Choose My Practice
Expertise in Advanced Treatments: I specialise in the most sophisticated melanoma treatments available, including immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and precision radiotherapy.
Cutting-Edge Technology: Access to MR-linac, stereotactic radiotherapy, and other advanced technologies not widely available.
Personalised Care: Every treatment plan is tailored to your specific melanoma characteristics and individual circumstances.
Rapid Access: Appointments available within 1-2 days, with results and treatment plans expedited. I simply will not accept delays when it comes to your care.
Continuity of Care: You’ll see me personally at every appointment, ensuring consistent, expert care throughout your journey.
Private Healthcare Advantages
Choosing private melanoma care offers several important benefits:
- Immediate access to consultations and investigations
- No delays in starting treatment
- Access to the latest technologies and treatments
- Comfortable, private treatment environments
- Direct communication with your specialist
- Coordinated care across multiple London locations
London Clinic Locations
I practice at four leading London hospitals, each offering state-of-the-art facilities:
LOC - Harley Street 95 Harley Street, London, W1G 6AF
LOC - Sydney Street 102 Sydney Street, London, SW3 6NJ
The London Clinic 20 Devonshire Place, London W1G 6BW, United Kingdom
The Cromwell Hospital 164-178 Cromwell Road, London SW5 0TU, United Kingdom
Prevention and Early Detection
While not all melanomas can be prevented, significant risk reduction is possible through protective measures and vigilant monitoring.
Preventing Melanoma
Sun Protection Strategies
Effective sun protection forms the foundation of melanoma prevention:
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen: Apply SPF 30 or higher sunscreen daily, reapplying every two hours
- Seek shade: Avoid direct sun exposure, especially between 10 AM and 4 PM
- Wear protective clothing: Long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses
- Avoid tanning beds: Artificial UV radiation significantly increases melanoma risk. The use of sunbeds baffles me!
Lifestyle Choices to Reduce Risk
Additional prevention strategies include:
- Regular skin self-examinations
- Professional skin checks, especially for high-risk individuals
- Maintaining a healthy immune system through proper nutrition and exercise
- Avoiding severe sunburn, particularly in childhood
Early Detection Strategies
Regular Skin Self-Exams
Monthly skin self-examinations help identify changes early:
- Examine your entire body in good lighting
- Use mirrors to check hard-to-see areas
- Look for the ABCDE warning signs
- Document any concerning changes with photos
- Have a family member help check areas you can’t see clearly
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you notice:
- Any new mole or growth
- Changes in an existing mole
- A sore that doesn’t heal
- Unusual bleeding or itching
- Any spot that looks different from your other moles
The Importance of Regular Monitoring
For individuals at higher risk, including those with:
- Family history of melanoma
- Personal history of skin cancer
- Multiple or atypical moles
- Fair skin with freckling
- Previous organ transplant
Regular professional skin examinations are essential, typically every 6-12 months or as recommended by your healthcare professional.
Melanoma Treatment: A Personalised Approach
Effective melanoma treatment requires careful consideration of multiple factors to develop the most appropriate strategy for each individual patient.
Factors Influencing Treatment Decisions
Treatment planning considers:
- Stage and characteristics of your melanoma
- Location and size of the primary tumour
- Presence of genetic mutations (such as BRAF)
- Your general health and medical history
- Personal preferences and lifestyle factors
Treatment by Stage
Early Stage Melanoma (Stages 0-II)
For early-stage melanoma, treatment typically involves:
- Surgical excision: Removal of the melanoma with appropriate margins
- Sentinel lymph node biopsy: To check for microscopic spread
- Adjuvant therapy: For high-risk cases, additional treatment may be recommended to reduce recurrence risk
- Noeadjuvant therapy: For Stage III melanoma, additional treatment before surgery may be recommended to reduce recurrence risk
Advanced Melanoma (Stages III-IV)
Advanced melanoma requires a comprehensive approach:
- Systemic therapy: Immunotherapy or targeted therapy
- Radiation therapy: For symptom control or to treat specific metastases
- Surgical intervention: When appropriate for accessible metastases
- Clinical trials: Access to experimental treatments
Integrating Multiple Treatment Modalities
Modern melanoma care often involves combining different treatments:
- Neoadjuvant therapy: Treatment before surgery to shrink tumours
- Adjuvant therapy: Post-surgical treatment to prevent recurrence
- Maintenance therapy: Ongoing treatment to control advanced disease
- Supportive care: Managing side effects and maintaining quality of life
Living with Melanoma
A melanoma diagnosis affects not just physical health but emotional wellbeing and lifestyle. Comprehensive support addresses all aspects of your experience.
Managing Treatment Side Effects
Modern melanoma treatments, while highly effective, can cause side effects:
Immunotherapy side effects may include fatigue, skin reactions, and immune-related effects on organs. These are generally manageable with appropriate monitoring and intervention.
Targeted therapy side effects often include skin changes, digestive effects, and fatigue. Most side effects are mild to moderate and improve with time.
Radiation therapy side effects depend on the treatment area but are typically well-tolerated with modern techniques.
Emotional Support and Resources
Cancer diagnosis naturally causes anxiety and stress. Support resources include:
- Specialist nurse support throughout treatment
- Access to counselling services
- Support groups for melanoma patients
- Cancer information services e.g MacMillan Cancer Support
- Family support and education
Long-term Follow-up Care
Melanoma survivors require ongoing monitoring:
- Regular clinical examinations
- Imaging studies as appropriate
- Skin surveillance for new melanomas
- Management of late effects from treatment
- Lifestyle guidance for optimal health
Understanding Treatment Outcomes
Modern melanoma treatment has achieved remarkable improvements in survival rates and quality of life outcomes.
Survival Rates by Stage
Treatment success varies by stage at diagnosis:
- Stage I melanoma: 5-year survival rates exceed 95%
- Stage II melanoma: 5-year survival rates range from 80-95%
- Stage III melanoma: 5-year survival rates vary from 40-80% depending on extent of spread
- Stage IV melanoma: Significant improvements with modern treatments, with many patients achieving long-term control
Factors Affecting Prognosis
Several factors influence outcomes:
- Thickness of the primary tumour: Thinner melanomas have better prognosis
- Presence of ulceration: Intact skin surface indicates better outcomes
- Lymph node involvement: Number and extent of affected nodes
- Genetic characteristics: BRAF mutation status and other molecular features
- Patient factors: Age, general health, and immune function
Success with Modern Treatments
Recent advances have dramatically improved outcomes:
- Immunotherapy has transformed survival for advanced melanoma
- Targeted therapies provide rapid responses for BRAF-positive melanomas
- Combination approaches enhance effectiveness
- Precision radiotherapy improves local control with fewer side effects
This PET scan example from one of my patients demonstrates an almost complete metabolic response to immunotherapy, with previously active melanoma deposits no longer detectable—representing the remarkable potential of modern treatment approaches. We successfully treated the left lung nodules with SABR to eradicate all sites of disease!
Frequently Asked Questions
What does melanoma skin cancer look like?
Melanoma can appear in various forms. Early melanoma often looks like an unusual mole with irregular features—asymmetry, irregular borders, multiple colours, large diameter, or changes over time. However, some melanomas may appear as new dark spots, sores that don’t heal, or changes in existing moles. Amelanotic melanoma may appear pink or flesh-coloured rather than dark brown or black.
Is melanoma skin cancer curable?
Yes, melanoma is highly curable when detected early. Stage I melanomas have cure rates exceeding 95%. Even more advanced melanomas can often be controlled for long periods with modern treatments. The key is early detection and appropriate treatment with the latest therapies.
How fast does melanoma skin cancer spread?
The rate of melanoma progression varies significantly. Some melanomas grow slowly over months or years, while others, particularly nodular melanoma, can progress rapidly. This variability underscores the importance of immediate evaluation of any suspicious skin changes.
What causes melanoma skin cancer?
The primary cause is DNA damage from ultraviolet light exposure, whether from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. Other factors include genetic predisposition, family history of skin cancer, fair skin, and having many moles. Some melanomas occur in areas not typically exposed to sun, suggesting additional unknown factors.
How do I know if I have melanoma skin cancer?
Watch for the ABCDE signs: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Colour variation, Diameter over 6mm, and Evolution (changes over time). Any new mole, changing existing mole, or unusual skin growth should be evaluated promptly by a healthcare professional. Regular skin self-examinations help identify concerning changes.
Can melanoma skin cancer be inherited?
While most melanomas are not directly inherited, genetic factors can increase risk. Having a family history of melanoma increases your risk, and certain inherited genetic syndromes predispose to melanoma. If you have a strong family history of skin cancer, genetic counselling may be beneficial.
What are the survival rates for melanoma?
Survival rates depend on the stage at diagnosis. Early-stage melanomas have excellent cure rates, while advanced melanomas require more intensive treatment. However, survival rates for advanced melanoma have improved dramatically with modern immunotherapy and targeted treatments.
Does melanoma skin cancer itch?
Melanoma may cause itching, though this isn’t always present. Changes in sensation, including itching, tenderness, or pain in a mole, can be warning signs. However, many melanomas don’t cause symptoms, emphasising the importance of visual monitoring.
How is melanoma skin cancer treated?
Treatment depends on the stage and characteristics. Early melanomas are typically treated with surgical excision. Advanced melanomas may require combination approaches including immunotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, and surgery. I specialise in integrating the latest options to treat melanoma for optimal outcomes.
Is melanoma the most dangerous skin cancer?
Yes, melanoma is considered the most dangerous form of skin cancer due to its potential to spread to other parts of the body. However, when caught early, it’s highly treatable. Non-melanoma skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma rarely spread and have excellent cure rates.
Take the Next Step in Your Melanoma Care
If you’re concerned about melanoma skin cancer or have been recently diagnosed, expert care is essential. Early intervention with the most advanced treatments available provides the best possible outcomes.
Scheduling Your Consultation
I offer rapid access to consultations, typically within 1-2 days of contact. During your appointment, we’ll:
- Review your medical history and examine any concerning lesions
- Arrange appropriate investigations if needed
- Develop a personalised treatment plan
- Answer all your questions about melanoma and treatment options
- Coordinate care with other specialists as needed
What to Expect
Your first appointment will be comprehensive and unhurried. I ensure you understand your diagnosis, treatment options, and what to expect throughout your care. You’ll receive copies of all correspondence and test results on the same day, keeping you fully informed about your treatment plan.
Contact Information
Don’t delay in seeking expert melanoma care. Contact my team today to arrange your consultation and begin the journey toward optimal treatment outcomes.
Call [+44 (0)20 7993 6716](tel:+44 (0)20 7993 6716) or email us to schedule your melanoma consultation.
Alternatively, you can book your consultation directly here.
Early detection and expert treatment provide the best chance for successful melanoma outcomes. Let me put my expertise and access to cutting-edge treatments to work in your fight against melanoma skin cancer.
The sooner we begin appropriate evaluation and treatment, the better your chances of successful outcomes. I’m committed to providing the highest standard of melanoma care, combining advanced medical expertise with compassionate, personalised attention throughout your treatment journey.